Description of the
Method
A FMEA is used to
examine each potential failure mode of a process to determine the effects of
the failure on the system. A failure mode is the symptom, condition, or fashion
in which hardware fails. It may be identified as a loss of function, a
premature function (function without demand), an out-of-tolerance condition, or
a physical characteristic, such as a leak, observed during inspection. The
effect of a failure mode is determined by the system's response to the failure.
Analysis Procedure
A FMEA has three
steps: (1) defining the process, (2) performing the analysis, and (3) documenting
the results. Defining the process for study and documenting the results can be
performed by a single person. The analysis itself must be performed by a team.
DEFINING THE PROCESS. This step
identifies the specific vessels, equipment, and instrumentation to be included
in the FMEA and the conditions under which they are analyzed. Defining the
problem involves establishing an appropriate level of resolution for the study
and defining the boundary conditions for the analysis.
The required level of
resolution determines the extent of detail needed in a FMEA. The choices for
the level of resolution range from the subcomponent level to the system level. To
satisfy PSM Rule requirements, most FMEAs should be performed at the major component
level. This level provides the best trade-off between the time necessary to perform
the analysis and the usefulness of the information gained from it.
Defining the analysis
boundary conditions requires the following.
1.
Identifying
the system or process to be analyzed.
2.
Establishing
the physical boundaries of the system or process.
3.
Establishing
the analytical boundaries of the system or process.
4.
Documenting
the internal and interface functions.
5.
Documenting
the expected performance of the system, process, or equipment item; the system
or process restraints; and the failure definitions of the equipment items, the
process, or the system.
6.
Collecting
up-to-date information identifying the process equipment and its functional
relationship to the system.
Functional narratives
about the system or process should include descriptions of the expected
behavior of the system or process and the equipment components for each operational
mode. Narratives should describe the operational profiles of the components and
the functions and outputs of each.
To assist in the
review, block diagrams should be constructed which illustrate the operation, interrelationships,
and interdependencies of functional components for each equipment item. All
interfaces should be indicated in these block diagrams.
PERFORMING THE
ANALYSIS.
The FMEA should be performed in a deliberate, systematic manner to reduce the
possibility of omissions and to enhance completeness. All failure modes for one
component should be addressed before proceeding to the next component. A
tabular format is recommended for recording results. A FMEA worksheet is
produced by beginning at a system boundary on a reference drawing and
systematically evaluating the components in the order in which they appear in
the process flow path. A worksheet such as that shown in Fig.1 should be
completed for each equipment item, as follows.
Failure Mode. The PrHA team should
list all of the equipment item and interface failure modes. Given the
equipment's normal operating condition, the team should consider all conceivable
malfunctions.
Cause(s). If desired, the root
causes of the failure mode should be identified. Identification of root causes
provides information helpful for ranking hazards.
Operational Mode. If the equipment being
analyzed is subject to different modes of operation, each operational mode
should be identified and analyzed separately.
Effects. For each identified
failure mode, the PrHA team should describe the anticipated effects of the
failure on the overall system or process. The key to performing a consistent
FMEA is to assure that all equipment failures are analyzed using a common
basis. Typically, analysts evaluate effects on a worst-case basis, assuming
that existing safety levels do not work. However, more optimistic assumptions
may be satisfactory as long as all equipment failure modes are analyzed on the
same basis.
Failure Detection
Method. The
means of failure detection should be identified, such as visual or warning
devices, automatic sensing devices, sensing instrumentation, or other
indicators. The main purpose of identifying failure detection methods is to
determine whether the failure mode is "hidden," i.e., not detectable
for some period of time. If there is no means to detect failure, "none"
should be entered into the worksheet.
Compensating
Provisions. For
each identified failure mode, the PrHA team should describe any design
provisions, safety or relief devices, or operator actions that can reduce the
likelihood of a specific failure or mitigate the consequences.
Severity Class. The severity of the
worst consequence should be specified as follows.
Category I - Catastrophic - May cause death or loss of
system or process.
Category II - Critical
- May cause severe injury, major property damage, or major system damage.
Category III - Marginal
- May cause minor injury, minor property damage, or minor system damage.
Category IV - Minor -
Is not serious enough to cause injury, property damage, or system damage, but
may result in unscheduled maintenance or repair.
Remarks/Actions. For each identified
failure mode, the PrHA team should suggest actions for reducing its likelihood
or mitigating its effects. The actions suggested for a particular piece of equipment
may focus on the causes or effects of specific failure modes or may apply to
all of the failure modes collectively.
If the team discovers
that a single item failure is not detectable, the FMEA should be extended to
determine if the effects of a second failure in combination with the first
could have catastrophic consequences. When a safety, redundant, or back-up
component is evaluated, the analysis should consider the conditions that
generated the need for the component.
DOCUMENTING THE
RESULTS.
A FMEA generates a qualitative, systematic reference list of equipment, failure
modes, and effects. The results of a FMEA are usually listed in tabular format,
by equipment item. Fig.1 shows a typical worksheet used in performing a FMEA.
Fig.1
Example FMEA Worksheet
For each equipment
item, the failure modes for that item and, if desired, the root causes for that
failure mode are identified. For each failure mode, a worst-case estimate of
the consequences is identified. This worst-case estimate assumes the failure of
all protection against both the failure itself and the undesired consequences
of the failure. The method by which the failure is detected is specified along
with any compensating provisions. Finally, any suggestions for improving safety
are listed in the table.
The PSM Rule requires
that a FMEA be performed by a team, all of whose members participate in the
analysis. The most practical means of performing the FMEA is to prepare blank worksheets
on viewgraphs or on a large display screen. For each equipment item, the PrHA team
reaches a consensus on its failure modes and their causes, effects, detection
methods, compensating provisions, severity (if desired), and any remarks or
action items.
Staff requirements
for a FMEA vary with the size and complexity of equipment items being analyzed.
The time and cost of a FMEA is proportional to the size of the process and number
of components analyzed. On average, an hour is sufficient to analyze two to
four equipment items. For processes or systems in which similar equipment items
perform similar functions, the time requirements for completing a FMEA are
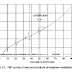
reduced. Fig.2 presents estimates of the time needed to perform a PrHA using
the FMEA method (CCPS, 1992).
Fig.2 Time
Estimates for Using the Failure Mode and Effects Analysis Method
Limitations of
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Human operator errors
are not usually examined in a FMEA, but the effects of human error are indicated
by an equipment failure mode. FMEAs rarely investigate damage or injury that
could arise if the system or process operated successfully. Because FMEAs focus
on single event failures, they are not efficient for identifying an exhaustive
list of combinations of equipment failures that lead to accidents.
Example Failure Mode
and Effects Analyses
Fig.3
Partial FMEA for Dock 8 HF Supply System
Fig.4 Partial
FMEA for the Cooling Water Chlorination System

.png)


.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)

.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
.png)
